More Quizzes
In our daily life we come across many occasions or incidents in which we need to describe whatever happened. Mostly it includes what someone said, what someone told or what someone asked. We speak naturally and spontaneously to describe all those situations.
Obviously, such kinds of situations automatically form two categories of our speech-
WHAT IS DIRECT SPEECH?
- Direct Speech is the report of the speaker using his own words exactly.
- Direct Speech is the repetition of the person’s words directly.
- Direct Speech is the group of unchanged words presented as they are, with quotation marks.
e.g. George said, “I am very much interested to study English Grammar now.”
WHAT IS INDIRECT SPEECH?
- Indirect Speech is the report of what another person said, told or asked.
- Indirect Speech is the content which is expressed in our own words, without quotation marks.
- Indirect Speech is the conveyance of the statement without changing its meaning.
e.g. George said that he was very much interested to study English Grammar then.
DIFFERENT CHANGES OCCUR IN INDIRECT SPEECH
A. CHANGES IN PRONOUNS
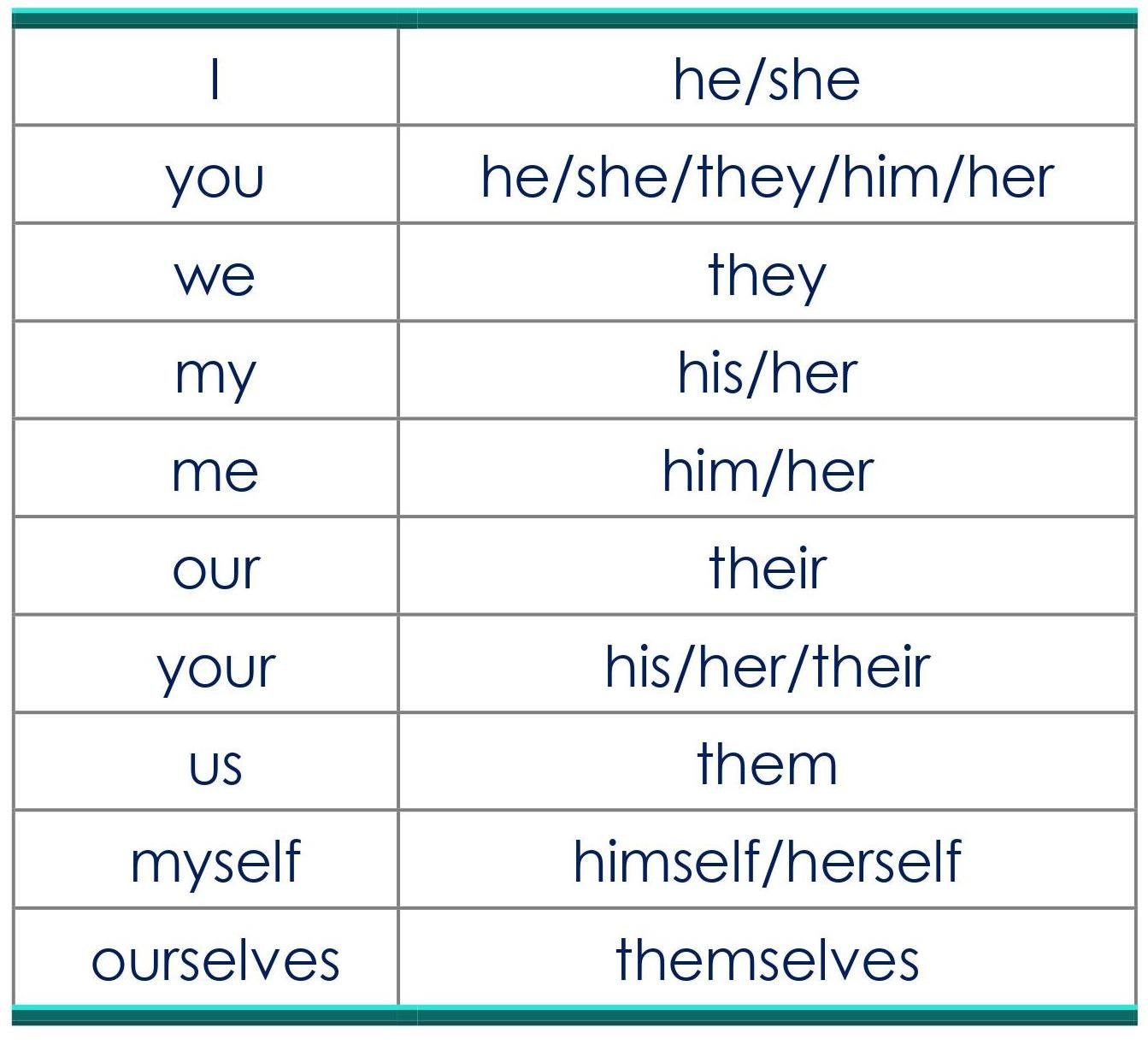 B. CHANGES IN VERBS
B. CHANGES IN VERBS
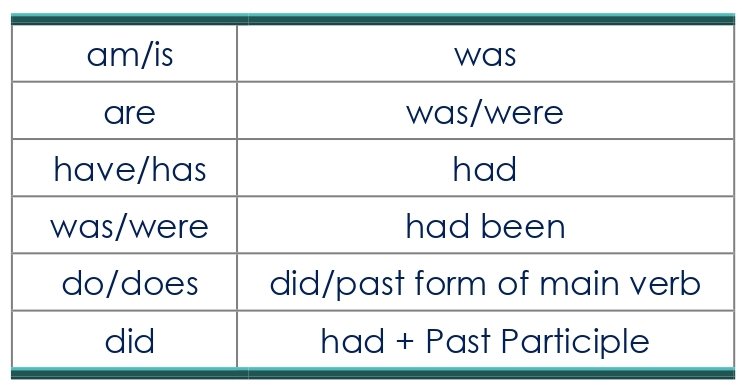 C. CHANGES IN MODAL AUXILIARIES
C. CHANGES IN MODAL AUXILIARIES
 D. CHANGES IN TIME AND PLACE ADVERBIALS
D. CHANGES IN TIME AND PLACE ADVERBIALS
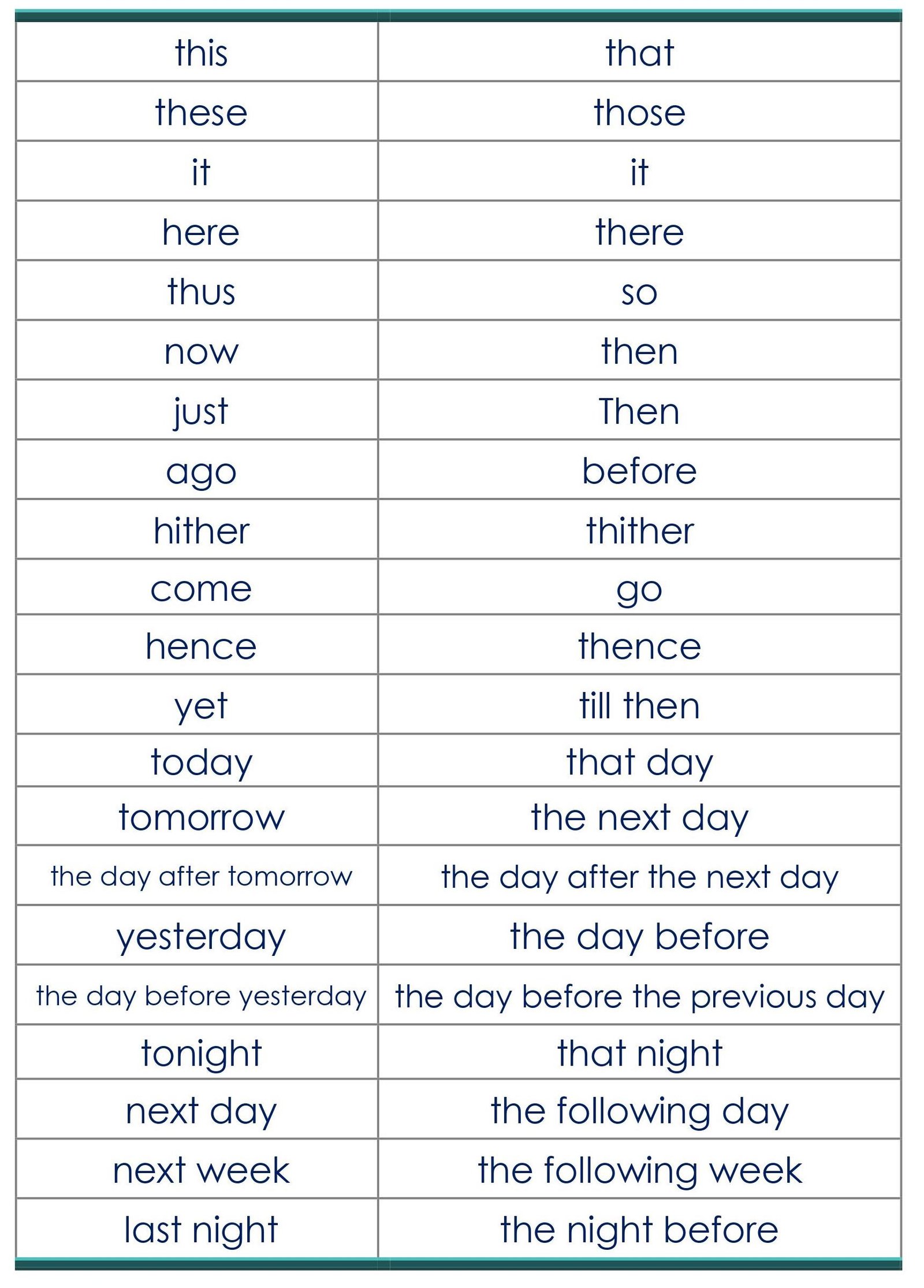 E. CHANGES IN TENSES
E. CHANGES IN TENSES
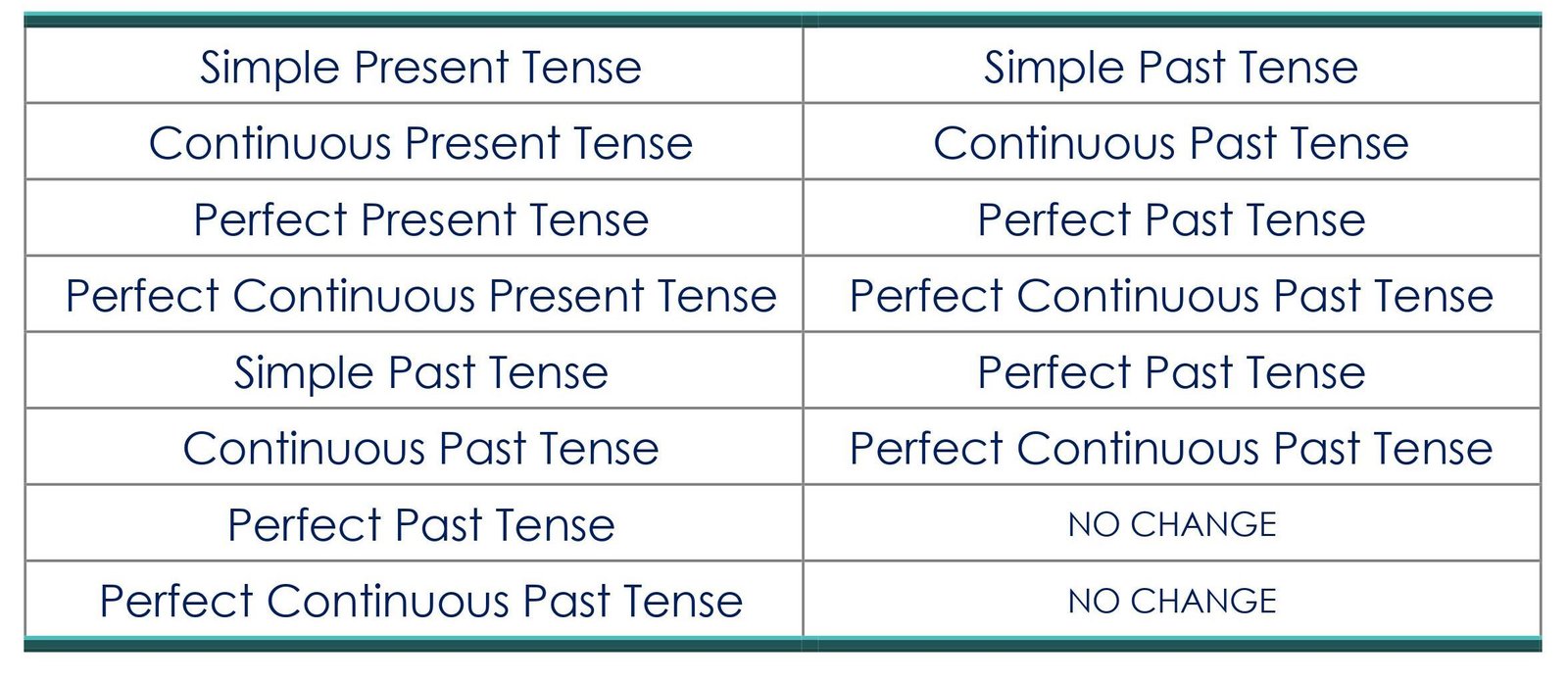 F. IMPORTANT RULE
F. IMPORTANT RULE
DIFFERENT USES OF DIRECT-INDIRECT SPEECH
A. IN DECLARATIVE SENTENCES
Declarative Sentence is the kind of sentence which makes an informative statement. It declares something directly.
General Rules–
i. remove comma and use conjunction ‘that’
ii. remove quotation marks
iii. change pronouns, verbs and adverbs properly
iv. change tenses properly
Examples–
Direct– Beatrice said, “I want to go to California tomorrow.”
Indirect– Beatrice said that she wanted to go to California the next day.
Direct– The teacher said, “I have been teaching English since 1996.”
Indirect– The teacher said that he had been teaching English since 1996.
Direct– Adam said to Calvin, “We are going to visit India next week.”
Indirect– Adam told Calvin that they were going to visit India next week.
Direct– Craig said, “I have given some books to my brother now.”
Indirect– Craig said that he had given some books to his brother then.
Direct– Father said to Samantha, “You need to take your medicines tonight.”
Indirect– Father told Samantha that she needed to take her medicines that night.
Direct– She says, “We are going to watch the football match.”
Indirect– She says that they are going to watch the football match.
Direct– Ralph will say, “Our plan is to solve these problems now.”
Indirect– Ralph will say that their plan is to solve these problems now.
Direct– She said, “I am ready to show my talent today.”
Indirect– She said that she was ready to show her talent that day.
Direct– Amy said, “My father helped me to solve these examples.”
Indirect– Amy said that her father had helped her to solve those examples.
Direct– Thomas said to his son, “You can come with me to meet your teacher.”
Indirect– Thomas told his son that he could come with him to meet his teacher.
B. IN INTERROGATIVE SENTENCES
Interrogative Sentence is the kind of sentence which asks a direct question. It enables us to answer and gather information. There are two types of Interrogative Sentences.
a. ‘Yes/No’ type question- begins with helping verb
b. ‘Wh’ question- begins with ‘Wh’ word
General Rules–
i. remove comma and use conjunction ‘if/whether’ in ‘Yes/No’ type
ii. remove comma and use same ‘Wh’ word as conjunction in ‘Wh’ type
iii. remove quotation marks and question mark
iv. use reported verb ‘asked’.
v. Make changes giving S+V+O sequence
vi. change pronouns, verbs and adverbs properly
vii. change tenses properly
Examples–
Direct– John said Ralph, “Are you going to buy a new shirt today?”
Indirect– John asked Ralph if he was going to buy a new shirt that day.
Direct– The teacher said to students, “Have you completed your homework?”
Indirect– The teacher asked students if they had completed their homework.
Direct– Bella said, “Smith, do you really want to leave this college?”
Indirect– Bella asked Smith whether he really wanted to leave that college.
Direct– The Professor said, “Is there any question to ask now?”
Indirect-The Professor asked if there was any question to ask then.
Direct– Rehan said to Ahmed, “Did you go to meet your uncle yesterday?”
Indirect– Rehan asked Ahmed if he had gone to meet his uncle the day before.
Direct- I said to my mother, “What were you writing in the notebook?”
Indirect- I asked my mother what she had been writing in the notebook.
Direct– George said to me, “Where have you gone the day before yesterday?”
Indirect– George asked me where I had gone the day before the previous day.
Direct– Father said, “Where does your English teacher live in this area?”
Indirect– Father asked where his English teacher lived in that area.
Direct– Mrunal said to Riya, “How long are you staying here in Mumbai?”
Indirect– Mrunal asked Riya how long she was staying there in Mumbai.
Direct– The coach said to players, “Why are you late today?”
Indirect– The coach asked players why they were late that day.
C. IN IMPERATIVE SENTENCES
Imperative Sentence is the kind of sentence which issues a request, command, advice or suggestion. They tell us what to do, using different tones.
General Rules–
i. remove ‘said’ or ‘said to’, use appropriate reported verb
(e.g. requested, ordered, suggested, advised, warned etc.)
ii. remove comma and use conjunction ‘to’ or ‘not to’
iii. remove quotation marks and question mark
iv. change pronouns, verbs and adverbs properly
v. remove ‘Please’, use reported verb ‘requested’
vi. if sentence begins with ‘Let’s’, three changes occur-
a. remove ‘Let’s’, use reported verb ‘suggested’,
b. use conjunction ‘that’
c. begin the sentence with ‘they should….’
(because ‘Let’s’ means ‘we shall’)
Examples–
Direct– Alice said to Callie, “Give me the ink-pen for today.”
Indirect– Alice requested Callie to give her the ink-pen that day.
Direct– The old passenger said, “Please offer me your seat for some time.”
Indirect– The old passenger requested to offer him his seat for some time.
Direct– Javed said, “Let’s play basketball on the ground.”
Indirect– Javed suggested that they should play basketball on the ground.
Direct– The doctor said, “Quit smoking from today.”
Indirect–The doctor advised to quit smoking from that day.
Direct–The teacher said to me, “Do not make a noise.”
Indirect– The teacher warned me not to make a noise.
Direct– The commander said, “Fire at the enemy.”
Indirect– The commander commanded to fire at the enemy.
Direct– Father said to son, “Use mask at public places.”
Indirect– Father advised son to use mask at public places.
Direct– The teacher said to students, “Write your papers with blue ink-pen.”
Indirect– The teacher suggested students to write their papers with blue ink-pen.
Direct– The officer said, “Clean my office in half an hour.”
Indirect– The officer ordered to clean his office in half an hour.
Direct– Lilian said, “Remember to send an email at 6 o’clock.”
Indirect– Lilian reminded to send an email at 6 o’clock.
D. IN EXCLAMATORY SENTENCES
Exclamatory Sentence is the kind of sentence which contains a strong emphasis, emotion, feeling or excitement.
General Rules–
i. remove ‘said’ or ‘said to’, use reported verb ‘exclaimed’
ii. remove comma and use conjunction ‘that’
iii. convert exclamatory into assertive, wherever necessary
iv. change pronouns, verbs and adverbs properly
v. change tenses properly
Examples–
Direct– Harper said, “What a beautiful sight it is!”
Indirect– Harper exclaimed that it was a very beautiful sight.
Direct– Jennifer said, “How difficult the paper is!”
Indirect– Jennifer exclaimed that the paper was very difficult.
Direct– All players said, “Hurrah! We have won the match.”
Indirect– All players exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
Direct– He said, “Alas! his father is no more.”
Indirect– He exclaimed with sorrow that his father was no more.
Direct– She said, “How foolish my brother has been!”
Indirect– She exclaimed that her brother had been very foolish.
Direct– Garry said, “Ah! My kite is high up in the sky”.
Indirect– Garry exclaimed with great joy that his kite was high up in the sky.
Direct– He said, “What a hard work my father has been doing!”
Indirect– He exclaimed that his father had been doing a very hard work.
Direct– Aditya said, “My God! You have injured your head.”
Indirect– Aditya exclaimed shockingly that he/she had injured his/her head.
Direct– Doctor said, “Sorry! I can’t save your father.”
Indirect– Doctor exclaimed with regret that he couldn’t save his father.
Direct– Smith said, “Elena, how clever you are!”
Indirect– Smith exclaimed that Elena was very clever.
Grammar Topics_1
Grammar Topics_2
Useful Expressions in English Speaking
Grammar: Spot the Error








































Very nice sir
As usual this topic is also simplified.
It’s very useful for students of rural as well as urban area.
Thanks for sharing such simplified material of challenging topic.
Waiting for further topics & material
Very good activity sirji.it is helpful learners like me.
Regards
very nice 👍
Thanks sir,
Because it helps in study…🙏👍
It is very useful for every English learners .
Thanks .
Great, sir. Very useful
Really helpful ! these blog . I read these blog from that day its suggesting to my students and they also enjoying and getting marks .
Very nice
Thank you sir very useful
Very creative work. It’s very useful for students.
Thanks
Nice I like it
Thank you so much sir
I absolutely love your blog…
Very Nice sir
It is very nice sir its very helpful in studys.